On one of my SQL Server 2008 Instance, the msdb database sizes around 4 GB. I decided to find out the which table / index occupies major junk on this. I have used query below;
| --- Query 1, if there is partition SELECT TOP 10 SERVERNAME=@@SERVERNAME,DB_NAME=DB_NAME(),TABLE_NAME=OBJECT_NAME(I.ID),INDEX_NAME=I.NAME,INDID,USED, ROWS, SIZE_N_MB = ROUND((USED*8.0/1024.0),2), |
| --- Query 2 If there are partitions SELECT object_name(i.object_id) as objectName, |
The output resulted;
The following 5 big tables takes up 88% of the total database size of 3.8 GB. These 5 tables occupy 3.3 GB on the msdb database.
Query 1: Output
| TABLE_NAME | INDEX_NAME | INDID | USED | ROWS | SIZE_N_MB | ROWMODCTR | STATISTICDT |
| backupfile | PK__backupfi__57D1800A17C286CF | 1 | 233057 | 4438738 | 1820.76 | 2646909 | 2/14/2011 15:57 |
| backupset | PK__backupse__21F79AAB0E391C95 | 1 | 115791 | 1489763 | 904.62 | 228112 | 6/19/2011 6:00 |
| backupmediafamily | PK__backupme__0C13C86F0880433F | 1 | 50738 | 1489616 | 396.39 | 23386 | 7/26/2011 7:00 |
| backupfilegroup | PK__backupfi__760CD67A12FDD1B2 | 1 | 43284 | 2967333 | 338.16 | 1775145 | 2/14/2011 15:57 |
| backupmediaset | PK__backupme__DAC69E4D04AFB25B | 1 | 29250 | 1489616 | 228.52 | 44462 | 7/22/2011 15:43 |
| sysjobhistory | clust | 1 | 3553 | 33177 | 27.76 | 2428 | 7/25/2011 8:14 |
Query 2: Output
| objectName | indexName | totalPages | usedPages | dataPages | totalSpaceMB | usedSpaceMB | dataSpaceMB | Rows |
| backupfile | PK__backupfi__57D1800A17C286CF | 233073 | 233043 | 231653 | 1820 | 1820 | 1809 | 4438738 |
| backupset | PK__backupse__21F79AAB0E391C95 | 100217 | 100200 | 99826 | 782 | 782 | 779 | 1489763 |
| backupfilegroup | PK__backupfi__760CD67A12FDD1B2 | 43289 | 43283 | 43077 | 338 | 338 | 336 | 1489616 |
| backupmediafamily | PK__backupme__0C13C86F0880433F | 39473 | 39459 | 39287 | 308 | 308 | 306 | 2967333 |
| backupmediaset | PK__backupme__DAC69E4D04AFB25B | 18737 | 18728 | 18654 | 146 | 146 | 145 | 1489616 |
Analyze and find out the minimum and maximum date range date available
| SELECT COUNT(*) AS 'TotalRecords', |
Resolution:
The solution is we have to purge these MSDB Backup and Restore history tables
1. The sp_delete_backuphistory system stored procedure takes a single parameter - a cutoff date. Any data older than the supplied date is purged from the msdb tables.
2. The sp_delete_database_backuphistory system stored procedure allows you to delete historical backup data for a specific database. Unfortunately, this procedure does not offer the finer option of choosing a cutoff date. It's all or nothing.
3. sp_purge_jobhistory Removes the history records for a job.
4. Try considering creating indexes on the above said 5 tables, if no of rows are huge.
Source: http://weblogs.sqlteam.com/geoffh/archive/2008/01/21/MSDB-Performance-Tuning.aspx
| use msdb Create index IX_backupset_backup_set_id on backupset(backup_set_id) |
5. Alternatively, check when the statistics of these tables are last updated. Just run sp_updatestats. Just try sp_delete_backuphistory after the statistics are updated. The result is awesome! Very quick response.
Permanent Resolution
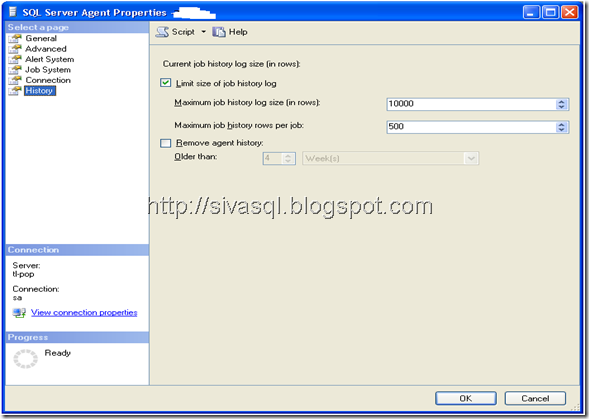
6. Further restrict the Job history growth by setting in SQL Agent –> History tab.
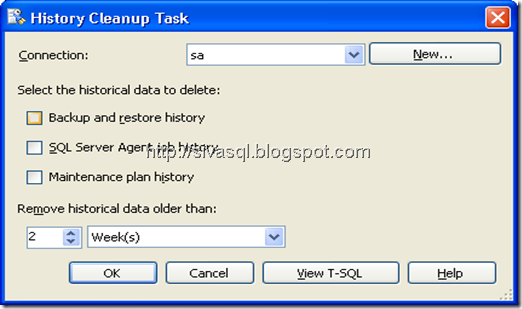
7. Also on the SQL Server Maintenance Plan “History Cleanup Task” can be of helpful
No comments:
Post a Comment